Explain Three Different Mechanisms for the Maintenance of Genetic Variation.
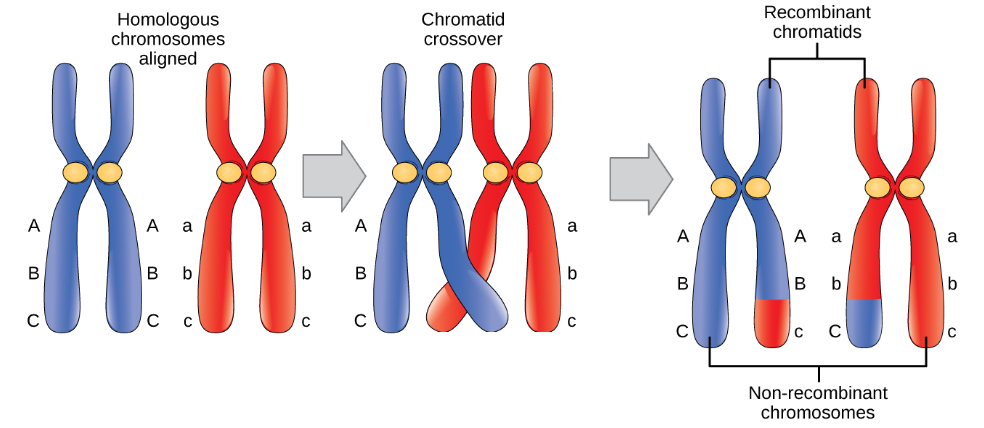
Crossing over or recombination between chromatids of homologous chromosomes during meiosis. Selection typically reduces variation.

How Prokaryotes Achieve Genetic Diversity Microbiology Health And Disease
Mutation is any change in an organisms DNA Most mutations are harmful to their bearers or are neutral but if environmental conditions change previously harmful or neutral alleles may.

. 1999 but see also Buonaccorsi et al. Genetic variation comes from mutations within DNA. Maintenance of genetic variation in personality through control of mental mechanisms.
Mutations are changes in the information contained in genetic material. So here are the situations that can maintain genetic variation in principle. A balance between mutation and selection.
Mutation increases genetic variation. Mutation Gene flow Genetic drift Nonrandom mating Natural selection Mutations Generate Genetic Variation Origin of genetic variation is mutation. And there can be negative frequency dependence.
There can be a balance between mutation and drift. Under balancing selection genetic variation is maintained rather than depleted by selection. The third possibility for explaining the maintenance of genetic variation in personality traits is balancing selection.
The developmental switch is therefore an anticipatory mechanism allowing different behavioural mating tactics. Click to see full answer. Genetic variation within a species can result from a few different sources.
Creates individuals with new combination of alleles. 3How genetic variation changes in populations over time. Finally genetic variation can be a result of sexual reproduction which leads to the creation of.
For most of life this means a change in the sequence of DNA A single mutation can have a. Explain three cellular andor molecular mechanisms that introduce variation into the gene pool of a plant or animal population. Genetic variation is essential for natural selection because natural selection can only increase or decrease frequency of alleles that already exist in the population.
Usually reduces genetic variation in. Genetic variation is caused by. 2001 for criticisms assortative.
A test of trust extraversion and agreeableness. A genetic barrier may result from a multitude of mechanisms including post-zygotic isolation such as hybrid breakdown endogenous factors or disruptive environmental selection exogenous factors pre-zygotic isolation mechanisms such as philopatry Fitzsimmons et al. Allele and genotype frequencies.
Genetic variation is the raw material for evolution. There are three primary sources of new genetic variation. There are four of them.
Explain the evolutionary mechanisms that can change the composition of the gene pool. Selective neutrality mutation-selection balance and. Pre-mating isolating mechanisms Geographical isolation.
However some forms of selection can maintain genetic variation. The human genome comprises about 3 10 9 base pairs of DNA and the extent of human genetic variation is such that no two humans save identical twins ever have been or will be genetically identical. How evolutionary change is measured.
For example frequency dependent or overdominant heterozygote advantage selection can maintain genetic variation. Maintenance of genetic variation in personality through control of mental mechanisms. Cross-level considerations for explaining selection pressures and the maintenance of genetic variation in condition-dependent male morphs.
Via these different mental mechanisms humans can respond to a wide variety of environmental challenges. While adopting a population-genetic view to explain genetic variation is important to. Three concepts to understanding evolution and natural selection.
There can be heterosis or over-dominance. And there can be negative frequency dependence. The transfer of genes from one population to another through the movement of individuals or their gametes.
Several researchers have attempted to explain the emergence and evolution of trust of strangers. There can be a balance between mutation and drift. Independent assortment of homologous chromosomes during meiosis I and of nonidentical sister chromatids during meiosis II.
Known evolutionary mechanisms. The usual mechanisms are divided into two different categories. Without genetic variation some key mechanisms of evolutionary change like natural selection and genetic drift cannot operate.
A balance between mutation and selection. Random fluctuations in allele frequencies as a result of chance result. So here are the situations that can maintain genetic variation in principle.
The process for generating different species who evolved from their original species they need to become isolated from one another in order to get a different mating and a specific genetic flow from the new formed group. We assess three evolutionary genetic mechanisms that could explain genetic variance in personality differences. The connection of these previously isolated gene pools through human intervention can lead to intraspecific diversity loss through extirpation of native populations or hybridization.
Genetic diversity also decreases the occurrence of unfavorable inherited traits. Random fertilization of an ovum by a sperm. Random genetic drift reduces genetic variation.
Migration can either increase or decrease genetic variation depending on. There are four of them. The three sources of genetic variability in a sexually reproducing organism are.
For example by selection pressures that fluctuate over time and space environmental heterogeneity that differ between the sexes sex-dependent selection or that. Another source is gene flow or the movement of genes between different groups of organisms. Crossing over between homologous chromosomes during prophase I.
Mutations the changes in the sequences of genes in DNA are one source of genetic variation. A heritable change in DNA. Terms in this set 10 Explain three cellular andor molecular mechanisms that introduce variation into the gene pool of a plant or animal population.
Random mating between organisms. Allopatric gene pools can evolve in different directions through adaptive and nonadaptive processes and are therefore a source of intraspecific diversity. How much genetic variation populations have.
The movement of genes from one population to another or gene flow. And new genetic combinations resulting from sex. There can be heterosis or over-dominance.
Invents alleles that never before existed in the gene pool. Between any two humans the amount of genetic variationbiochemical individualityis about 1 percent. 2The source of that variation.

How Prokaryotes Achieve Genetic Diversity Microbiology Health And Disease

Chapter 6 Genetic Diversity And Inbreeding Animal Breeding Groen Kennisnet Wiki

Comments
Post a Comment